ABCDEs of Melanoma: Recognizing Warning Signs for Early Detection
Safeguarding Your Skin
 Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, requires vigilance and awareness for early detection. Understanding the ABCDEs—Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter, and Evolution—can be a lifesaving tool in recognizing potential warning signs and seeking timely medical attention.
Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, requires vigilance and awareness for early detection. Understanding the ABCDEs—Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter, and Evolution—can be a lifesaving tool in recognizing potential warning signs and seeking timely medical attention.
Regular inspection crafts a narrative of resilience, ensuring your skin's well-being takes center stage.
Why Early Detection Matters
Prevention and Sun-Smart Practices
Asymmetry
The first letter in the ABCDEs, "A" stands for asymmetry. In melanomas, one half of the mole or spot is often different from the other half. Visualize a line through the center; if the two halves do not mirror each other, it's a potential warning sign.
Border Irregularity
"B" signifies border irregularity. Melanomas often have uneven, jagged, or notched edges. Unlike benign moles with smooth and well-defined borders, irregularity in the border of a spot may indicate a cause for concern.
Color Variations
"C" stands for color variations. Melanomas can exhibit an array of colors, including shades of brown, black, blue, or even red. Keep an eye out for spots with uneven coloring or a variety of hues within the same lesion, as this may signal melanoma.
Diameter
"D" denotes diameter. While not all melanomas are large, an increase in size can be a red flag. Generally, moles larger than six millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser) may warrant closer inspection. However, it's essential to remember that melanomas can also be smaller, emphasizing the importance of considering other ABCDE factors.
Evolution
The final letter, "E," highlights evolution. Monitor changes in the appearance of moles or spots over time. Any alterations in size, shape, color, or texture should be taken seriously. Rapid changes or evolution of a spot may indicate the need for prompt medical evaluation.
From Our QualDerm Family of Brands: Melanoma Treatment Options
Understanding the ABCDEs of Melanoma
Empower yourself with knowledge and vigilance by understanding the ABCDEs of melanoma. Regularly inspect your skin, looking for asymmetry, border irregularity, color variations, changes in diameter, and evolution of moles or spots. Early detection through these simple yet powerful guidelines can be the key to successful treatment and, ultimately, the preservation of your skin health. Remember, your skin deserves the best care, and your proactive efforts can make a significant impact in the fight against melanoma.
Featured Sunscreens
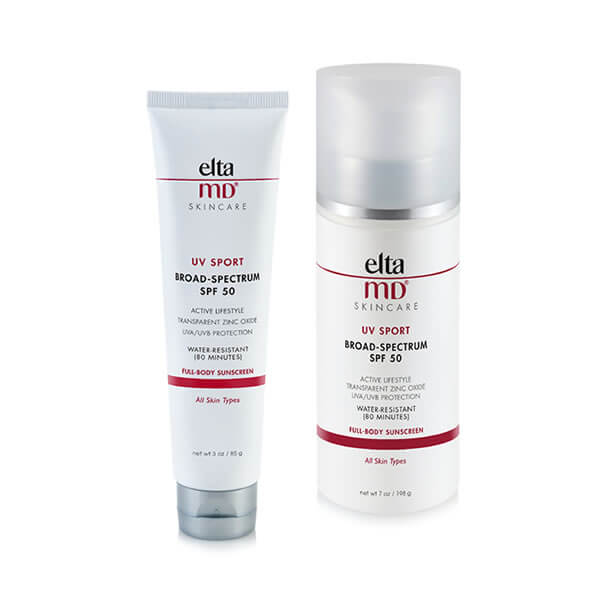

EltaMD UV Sport SPF 50 3oz, 7 oz
Have your fun in the sun – but play it safe. This sunscreen is great for swimmers, skiers, runners, golfers and other athletes – or for those who just love to be outdoors! UV Sport is water-resistant, so it won’t rinse off in water or drip into your eyes and sting when you sweat.
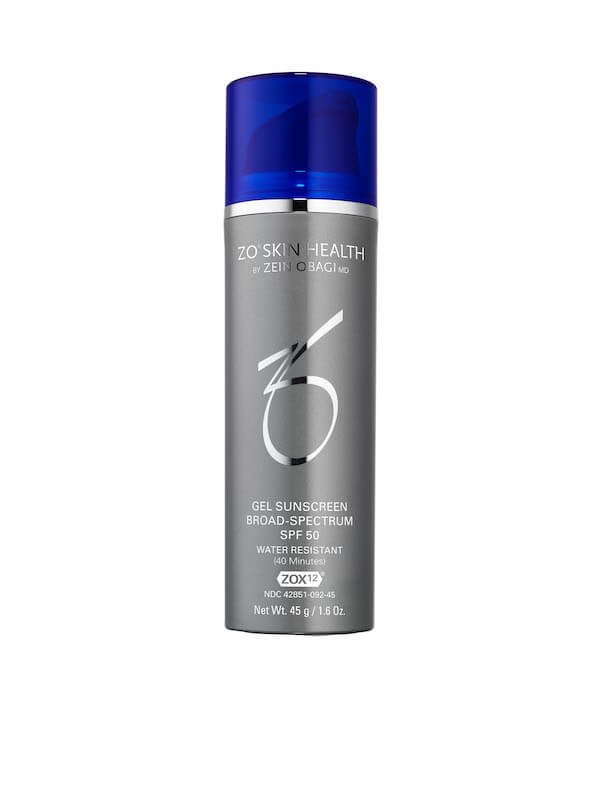

ZO® Gel Sunscreen Broad-Spectrum SPF 50
A clear and unscented gel sunscreen with a complexion-smoothing finish for all skin tones. Exclusive antioxidant + plant stem cell complexes minimize the aging effects of environmental aggressors. Water and sweat resistant up to 40 minutes. Fragrance-free. 45 g / 1.6 Oz.
Related Blog Posts
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
It’s time to face the facts: skin cancer can develop in individuals of all skin colors, including those with darker skin tones.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
In this blog, we’re covering what you need to know about five dangerous skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), malignant melanoma, merkel cell carcinoma, and kaposi sarcoma.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Navigating the landscape of Total Body Skin Exams: Uncover the comprehensive process, understand why it matters for skin health, and gain insights into what to expect during these essential dermatological examinations.
Read More